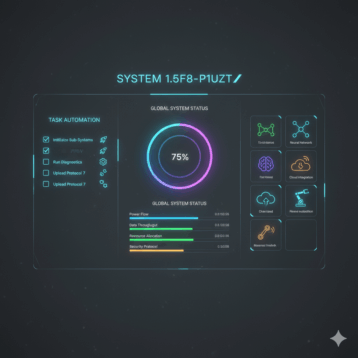
Cloud services refer to a wide range of technology services delivered on-demand to companies and individual customers over the Internet. These services are meant to provide affordable, easy access to resources and applications without the need for hardware or telecommunication infrastructure.
From document collaboration to checking email, billions of people today rely on the cloud for work and play, even without realizing it. Cloud services are offered and deployed by cloud computing service providers and vendors. They are hosted on the servers of the cloud services provider, then made available to end-users.
Advantages of Cloud Services
The cloud has found widespread use because of its compelling advantages, which include the following.
1. Scalability
The cloud service provider is responsible for all the underlying hardware and software. Therefore, users don’t have to purchase and install their own infrastructure or hire technology experts to manage it. For this reason, cloud services have a far higher degree of scalability than traditional on-premises infrastructure.
And scaling can be achieved almost instantly. All a user has to do is request an upgrade to a higher capacity plan and that new plan will be made available to them in a matter of minutes. Whether scaling is to accommodate an expanding workforce and growing need for memory space, cloud services fit the bill.
2. Lowered Costs
Cloud services benefit from economies of scale. They will set up top-notch infrastructure then sell or avail tiny fractions of the space and capacity to numerous subscribers. That allows them to split the cost across multiple users and, therefore, offer a highly competitive price for subscribers.
Users can pay a monthly or annual subscription that is much less than what they’d otherwise have to pay for software licenses and hardware acquisition. This is especially convenient for SMBs and individual users who don’t have the financial muscle to purchase top-notch technology.
3. Increased Flexibility
With cloud services, users subscribe on an as-needed, on-demand basis. If and when they no longer have a need for the platform or application, they can cancel the subscription and discontinue the service.
Compare this to on-premises setups where canceling is a more arduous process. The organization has already sunk finances into acquiring infrastructure and systems, so canceling it is difficult and expensive. Subscriptions cost little, so the organization doesn’t have to worry about the redundancy of their technology investment when they decide it’s time to drop it.
Main Types of Cloud Services
Cloud services are not created equal or identical. There isn’t a single type of cloud computing that’s suitable for everyone. Several different services, types, and models have evolved over the years to cater to different market needs. That said, most cloud computing services fall into three broad categories. They are sometimes referred to as the cloud ‘stack’ because they build on top of each other.
1. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
Software-as-a-service (SaaS) is the original and most widely recognized cloud service. It’s a broad category that encompasses web-based email, file storage, data backup, and project management tools.
Examples of SaaS providers include Office 365, G Suite, Dropbox, Citrix, and Slack. In each of these applications, users can create, store, share, and secure their data in the cloud.
2. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) makes available the infrastructure that cloud services require to manage SaaS tools, but do not want to manage the software that runs on it. It’s a complete data center solution that excludes on-site, resource-intensive installations. Examples of IaaS include Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Google Compute Engine.
These providers maintain networking hardware and storage servers, and may also offer application firewalls, load balancing, and more. In fact, many famous SaaS providers run on a third party’s IaaS platform.
3. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a service (PaaS) is a cloud service model that provides a web-based environment where programmers can develop cloud apps. PaaS provides the operating systems, programming languages, and databases that software companies would use to build apps without having to maintain these elements. Many IaaS providers will offer PaaS, as well.
As cloud services expand in function, sophistication, and availability, they’ll continue to find an ever wider range of applications.