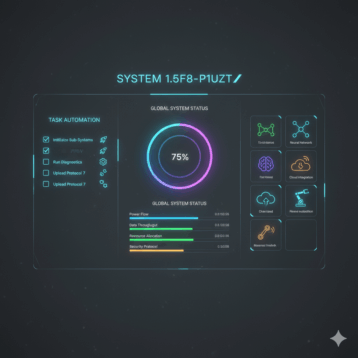
To get the most out of any business today, it is essential to ensure maximum customer satisfaction and maintain a streamlined, seamless workflow. Both of these key aspects are highly reliant on the company’s IT infrastructure management processes. Today we are going to focus on some of the critical aspects of IT infrastructure management, each of which must be optimized to maintain speed, productivity and quality in terms of both customer service and internal workflow.

Managing the Lifecycle of an IT Infrastructure
The IT management team handles all aspects of the internal and connected software infrastructure, from beginning to end. This includes everything from the planning, designing, implementing, securing and updating, to the disposal of the system when the time comes to do so. In other words, they are responsible for managing the entire lifecycle of a system.
Micromanagement
Micromanagement is an overly broad term used to describe countless tiny processes within the IT infrastructure, which must be monitored, catered to and updated as necessary. It’s a major bulk of the actual work which any IT management team is responsible for, and the system’s performance is mostly reliant on how good they are at micromanagement.
Network Monitoring and Security
As the Dallas based IT management and solutions provider Total IT explains, out of the multiple divisions of cybersecurity which are to be maintained within a business IT infrastructure, network monitoring (switches, routers, firewalls, associated software tools, etc.) and network security protocol management are absolutely crucial to a business’s survival today. Ignored or below-par network security can lead to data breaches and systemwide malware infections, followed by a whole list of consequences such as massive financial losses, tainted reputation and loss of clientele.
IT Alert Management
IT alerts are small tools put into place for monitoring significant changes, risky actions, suspicious activities and failures. On crossing the preset thresholds, the alerts would get activated and immediately inform the IT management team about them.
Incorporating Automation
From monitoring and alerting, to handling various micro adjustments within the system at all times, the use of automation in IT management is critical to optimizing workflow today. However, what makes modern automation tools different form the ones that came before them is that they are now powered by self-learning algorithms. This has minimized the need for manual intervention in mundane IT management tasks, as well as improving the overall performance of a system through constant, intelligent optimization.
Detecting, Preventing and Eliminating Threats
Threats not only come from external sources, but they may also come from the inside, or from an associated SaaS service. The IT manager’s job is to ensure that such threats are detected in advance before they can become threats, and consequently, take the necessary actions to eliminate the source’s threat status. Lastly, it should be noted that bottleneck situations related to IT infrastructure should be prevented with regular monitoring before they can happen. In case something does go wrong though, and a process is stuck somewhere, it falls upon the IT management and support team to troubleshoot it, so that workflow can resume again.