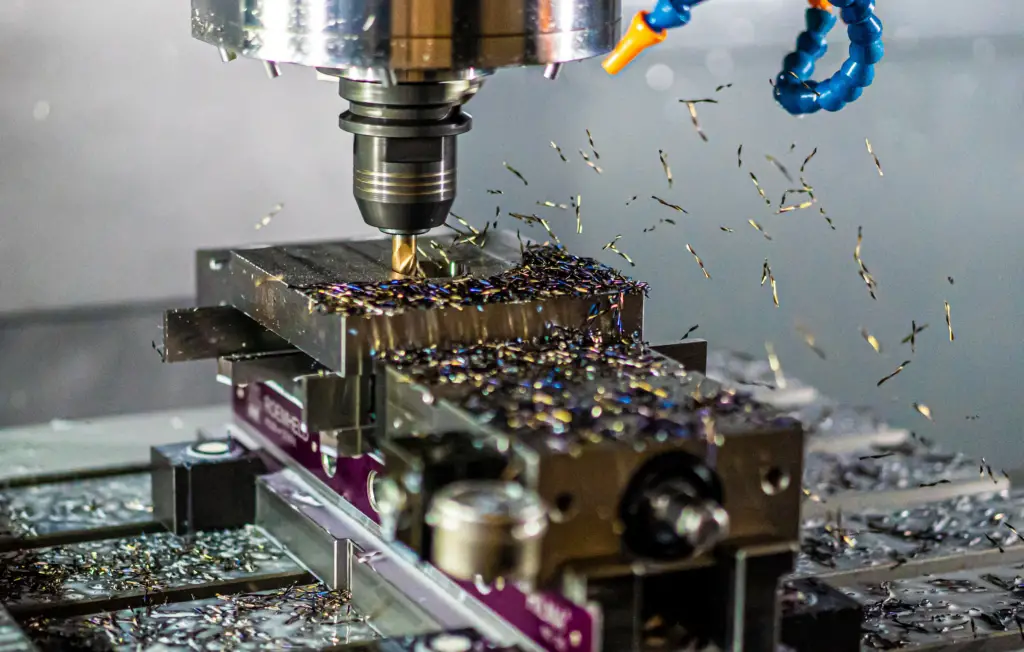
Nowadays, manufacturing (especially small-volume manufacturing) is different from how it was two or even a decade ago. Manufacturing technologies have advanced and, more importantly, so has the overall frame business is carried out in. If you enter a modern machine workshop or factory, you will see a lot of new equipment and machines as 5-axis and even 6-axis CNC machines have replaced their 3-axis predecessors, becoming the workshop staple over the past couple of decades.
Moreover, rapid prototyping and manufacturing have entered the scene, as they are complementary product development processes that are now widely utilized to produce numerous final products and their prototypes. Like CNC machines, rapid manufacturing equipment is even newer, along with the extensive use of production-ready 3D printers used in the last ten years. It changed rapid manufacturing in today’s modern production sites, and it’s expected that the industry will experience some exciting changes both in the short and long run.

Ten years ago, the product designers had to use a local supplier to manufacture or waste a few months setting up an international supply chain. Today, thanks to the internet and supplier management software, product manufacturers can order custom pieces from a manufacturer on the other side of the world in a matter of minutes. And the scene is continuously evolving further without any signs of slowing down.
Rapid manufacturing could take many different directions. In this article, we’re going through three major future trends that are expected to seriously influence on-demand rapid prototyping and manufacturing throughout the next couple of years.
Utilization Of Automation and Robotics For The Purpose Of Rapid Manufacturing
Needless to say that the future of manufacture will be partly shaped by the machines used by the producers of tomorrow. However, it’s hard to say what types of machinery will be utilized. Is the additive revolution going to keep its current rate, with new developments in fiber-based 3D printing transforming the creation of high-performance pieces? Or will modern technology be implemented in more traditional methods like casting?
The industry specialists can agree that in spite of the manufacturing method, automation and robotics will play a key role in the factories of the future. According to Global News Wire predictions, the automated 3D printing market is expected to grow to a staggering $8.9 billion by 2025. Also, MarketsandMarkets’ analysis on industrial automation showed that installing industrial robots reduces human interference in the production processes, lowering manufacturing costs, improving quality, and increasing production capacities.
Automation united with robotics allows factories to connect processes such as CNC machining, assembly, and surface processing. Also, it minimizes downtime between jobs and enables nighttime production without human oversight. Even though rapid manufacturing is less involved in production line automation than mass manufacturing, it will take advantage of technological developments such as improved process control and automated part removal.

The Availability Of Digital Spare Parts Libraries For Designers And Manufacturers
One of the responsibilities of each rapid manufacturing company is supplying pieces and materials on short-term notice, most probably in small amounts that meet the client’s demands. That responsibility will become even more significant in the years to come as companies begin to reconsider how they handle their inventory.
Companies that produce complex products like cars, industrial equipment, appliances, personal electronics, and sporting goods keep an inventory of spare parts. That enables them to service defective merchandise throughout a guarantee period or sell spare parts to their clients. Maintaining large inventory will demand warehouse space, stock management, and, most importantly, manufacturing parts that you might never use. But, many companies have to produce those parts, in case they might need them.
Given that many parts are now digitally designed with CAD software, the new method is to keep digital copies of those files and produce replicas of the necessary parts using a 3D printer, CNC machine, or a different rapid manufacturing tool. Companies can do that either on-site or via an outsourcing rapid manufacturing services company. There are two different approaches; you can choose between PPAP vs FAI.
As reported by Science Direct, researchers from a university in Finland found that long line products are great candidates for digital distribution. The digitalization results in cost reduction associated with lower transportation and warehousing costs and faster lead and delivery times.

The Appearance Of The Manufacturing As A Service (MaaS)
Last but not least, the future trend in the rapid manufacturing industry is already a major part of today’s on-demand components and prototypes scene. Besides, it is expected to expand in new and exciting directions. It is the growth in importance of MaaS platforms that utilize online systems to connect companies with manufacturers.
MaaS can be looked at as equivalent to the prevalence of short-term contracts of the modern workplace when employees are hired for individual projects and operations instead of retained as standard employees. Or you can compare MaaS to the car-sharing services, where users rent shared cars when they need them, paying much less than they would pay for having their own car. MaaS is made for companies that require various types of manufacturing procedures completed occasionally but for which it wouldn’t be cost-efficient to invest in their own equipment or workshop.
Gigantic MaaS platforms have become more and more beneficial to both manufacturers and clients. Thanks to MaaS, clients get a better feeling for the rapid manufacturing scene and launch their manufacturing projects faster, acquiring upfront costs and removing the time needed for the fee arrangements.
Final Words
All current business models are built upon the trends and possibilities that the manufacturing industry knows and foresees regarding manufacturing technologies and processes. For that reason, nowadays, companies expect to carry out their business online with minimum fuss, which means ordering a prototype as simple and as quick as hailing a cab or takeaway food and cutting their final product’s time to market by more than half.
If you’re in the manufacturing industry yourself, closely follow the dynamic nature of manufacturing and the new emerging technologies, stay informed on the latest trends on rapid manufacturing, and exploit as many possibilities within your production site as possible.