The idea that production processes could one day be almost entirely automated might have seemed sci-fi a few years ago, but as robots and cobots are becoming vital investments in all industries, business owners are beginning to understand that factory automation is finally here.
Experts define factory automation as “as the use of computer-aided control devices to operate different industrial processes by replacing human involvement.”
According to a Deloitte study, more than 30% of global shared services have implemented robotic automation, while 44% are in the process of planning and testing automation. Although many business owners are skeptical towards change and question whether automation can truly replace the human touch, research shows that, for certain processes, robots offer a series of benefits that can give businesses a competitive edge.
Nowadays, standard robot models can be mass-produced and the cost of implementing collaborative robots is also relatively low, making them a great investment for businesses that need to streamline processes.
What are the main types of robots used in the manufacturing process?
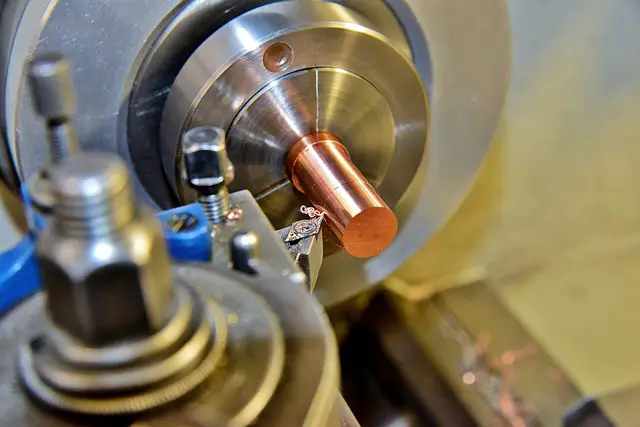
Welding robots
Welding robots account for 29% of all robots used in the manufacturing process. This is one of the most popular applications in the industrial sector and seven sub-categories of welding processes stand out: arc, resistance, spot, TIG, MIG, laser, and plasma welding. When they first came out, welding robots were only accessible to large enterprises, but, as their cost is beginning to decrease, plug-and-play welders are beginning to be used to small factories too.
Assembly robots
After welding, robot assembly is another key application of robot automation, accounting for 10% of all robots used in the manufacturing process. Whether they are employed to press-fit, insert, or disassemble parts, these robots have a quick installation process and can perform tasks faster and more safely than human workers.
Dispensing robots
Although they only account for about 4% of all robots used in the manufacturing process, dispensing robots still play an important part, because they make a painting, gluing, and spraying more accurate, even on rough and uneven surfaces.
Material removal robots
Material removal robots are very important at the end of the manufacturing process, where objects have to be polished through grinding, cutting, sanding or routing. By using material removal robots instead of human workers, employers can avoid the health risks caused by inhaling dust and toxic fumes.
Robot inspection systems
Although human workers now oversee the majority of inspection processes, robot inspection systems are on the rise. As the technology behind robot-based inspection system is becoming more advanced, soon robots could be used not just to verify if a machine component is present, but also to measure that component and assess its efficiency.
The key benefits of robotic automation for businesses

Although the presence of robots in factories is no longer regarded with the same skepticism, many people still fear that widespread automation could steal jobs and leave many workers without realistic job prospects.
According to the Office for National Statistics, automation could indeed replace 1.5 million jobs, the most at-risk being waiters, shelf fillers, elementary sales occupations, and catering assistants. However, at the same time, the jobs that could soon be automated are the high-risk or repetitive ones. The staff who did those jobs can be given other tasks where the human contribution is essential, and, ultimately, this will lead to extensive benefits for the company:
Reduced operational costs
Thanks to their accuracy, robots cause minimal material waste. At the same time, one single robot can perform the job of up to five people, which offers considerable savings to companies.
Worker safety
Human workers are exposed to health risks throughout every stage of the production process. From the use of heavy use machinery to the inhalation of toxic fumes, people can sustain serious injuries that can become life-threatening. By giving dangerous tasks to robots, business owners can avoid millions in damages and ensure that people do their jobs in a safe environment.
Faster production times
Human error can push back the launch of the finished product, and this can make businesses lose their competitive edge. Meanwhile, robots can work 24/7 without error, and this speeds up manufacturing by a considerable margin.
High-quality results
In the case of human workers, an increase in working speed correlates to a decrease in product quality. When processes are automated, speed doesn’t come at a cost and you will deliver the same quality.
Consistent product quality
Automated processes are consistent and controlled. No matter the task they are executing, robots can be programmed to do the same actions every time, which means there will be no inconsistencies between the final products.
Better placement of human talent
In the average factory, workers are overwhelmed by deadlines and repetitive tasks and have no time to focus on critical business processes. By giving these tasks to robots, the human workforce can be reassigned in key roles and thus deliver more value.
Versatility
Unlike humans, robots do not have learning curves and they can perform a certain task regardless of the conditions. Robots are also designed to fit in tight spaces, which means you can take advantage of every inch of floor and wall space.
Integration with existing business tools
Most businesses already use specialized hardware and software. Robots can be integrated with these tools immediately, which leads to streamlined processes and increased productivity.
Mitigate the risk of lower workforce availability
Although people are worried that robots could “steal jobs” today, the picture could look different a few decades from now. It is estimated that by the year 2040, more than 75 million baby boomers will retire and only half of them will be able to replace them. This will create a gap in the workforce, and robots will be able to take on those jobs.