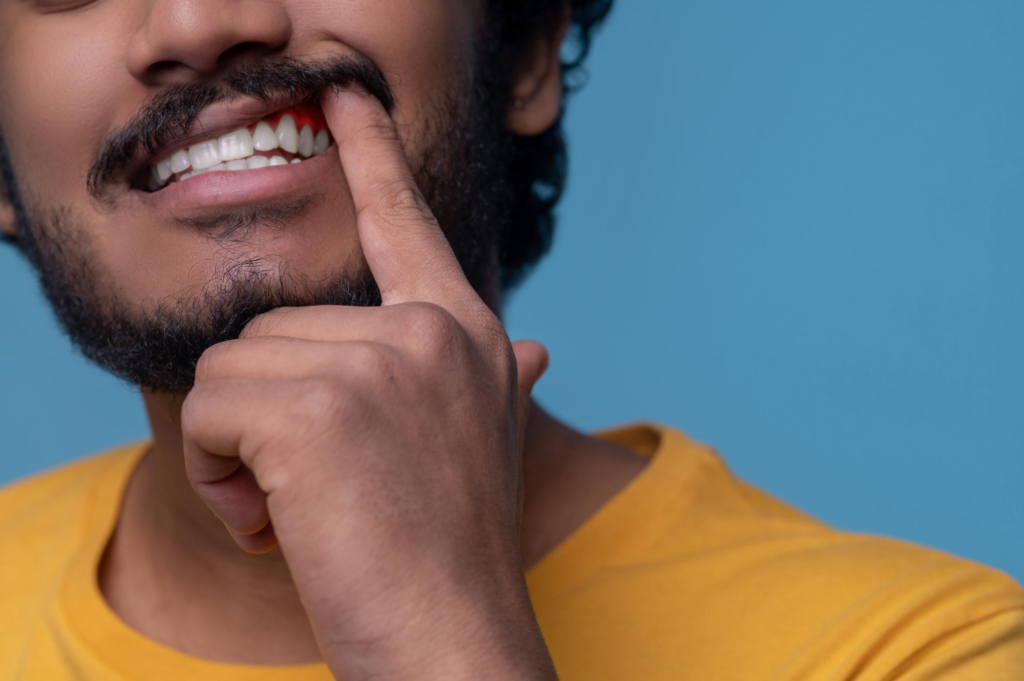
Gum disease remains one of the most common oral health conditions worldwide, yet the way dentists diagnose and treat it has changed significantly over time. What once relied heavily on basic cleaning and symptom management has evolved into a structured, evidence-based approach focused on early detection, targeted therapy, and long-term maintenance.
Today, gum disease treatment addresses the condition at every stage, from early gingivitis to advanced periodontitis. In Singapore, dental clinics increasingly adopt modern periodontal protocols that emphasize prevention, patient education, and minimally invasive care. This article explores how gum disease treatment has evolved, why these changes matter, and what patients can expect from contemporary dental care.
Understanding Gum Disease: Then and Now
Historically, gum disease often went unnoticed until symptoms became severe. Limited diagnostic tools made early detection difficult, and treatment focused primarily on visible signs rather than underlying causes.
Modern dentistry now recognizes gum disease as a chronic inflammatory condition driven by bacterial infection and host response. Dentists assess not only symptoms but also risk factors such as lifestyle habits, medical history, and oral hygiene practices. This broader understanding has reshaped gum disease treatment into a proactive, patient-centered process.
Gingivitis: Early Treatment Approaches and Modern Improvements
Traditional Management of Gingivitis
In the past, gingivitis treatment largely involved basic dental cleaning and general oral hygiene advice. While effective to a degree, these methods lacked personalization and follow-up.
Patients often received treatment only after noticeable bleeding or discomfort appeared, allowing inflammation to persist longer than necessary.
Modern Preventive Strategies
Today, dentists detect gingivitis earlier through routine screenings and digital documentation. Modern gum disease treatment emphasizes prevention through education, professional cleaning, and regular monitoring.
Patients receive tailored advice based on individual risk factors, improving compliance and outcomes. Early intervention now prevents progression more effectively than in previous decades.
Periodontitis: A Shift From Reaction to Management
Historical Treatment Limitations
Periodontitis once posed significant challenges due to limited understanding of its progression. Tooth extraction was common when infection advanced, as preserving damaged structures seemed impractical.
Treatment focused on managing symptoms rather than stabilizing the disease, often leading to tooth loss and compromised oral function.
Modern Periodontal Therapy
Advancements in periodontal science have transformed periodontitis care. Dentists now aim to control infection, preserve natural teeth, and maintain function.
Scaling and root planing, combined with structured maintenance, form the foundation of modern gum disease treatment. These techniques reduce bacterial load and promote gum healing without immediate resort to surgery.
Technological Advancements Shaping Gum Disease Treatment
Improved Diagnostic Tools
Digital X-rays, periodontal probing systems, and advanced imaging allow dentists to assess bone levels and gum health with greater accuracy. Early detection enables timely treatment, improving long-term outcomes.
Precision-Based Treatment Planning
Modern dentistry emphasizes precision. Dentists tailor gum disease treatment plans based on disease severity, patient habits, and response to previous care. This individualized approach contrasts sharply with earlier standardized treatments.
Minimally Invasive Solutions for Better Patient Experience
Non-Surgical Treatment Emphasis
Contemporary gum disease treatment prioritizes non-surgical solutions whenever possible. Improved instruments and techniques allow dentists to clean deep pockets effectively while minimizing discomfort.
Patients benefit from faster recovery times and reduced anxiety compared to traditional methods.
Targeted Antimicrobial Support
Localized antimicrobial therapies support mechanical cleaning in selected cases. These treatments enhance infection control without systemic medication, reflecting a more refined approach to periodontal care.
Surgical Treatment: Then and Now
Earlier Surgical Methods
Older surgical techniques often involved extensive tissue removal and longer healing times. While effective in controlling infection, these procedures sometimes compromised aesthetics and comfort.
Modern Periodontal Surgery
Today’s surgical interventions focus on tissue preservation and regeneration. Dentists use refined techniques to reduce pocket depth, encourage bone regeneration where possible, and improve long-term stability.
Surgery now represents a strategic option rather than a default response to advanced disease.
The Role of Maintenance in Modern Gum Disease Treatment
One of the most significant evolutions in periodontal care lies in long-term maintenance. Dentists now recognize gum disease as a condition requiring ongoing management rather than a one-time cure.
Patients with a history of gum disease benefit from regular maintenance visits that monitor progress, reinforce home care, and address issues early. This approach dramatically reduces recurrence rates.
Gum Disease Treatment in Singapore: A Modern Standard
Singapore’s dental care system reflects global best practices in periodontal management. Clinics operate under strict regulatory standards, ensuring evidence-based treatment and professional accountability.
Busy urban lifestyles increase gum disease risk locally, making preventive care essential. Many Singapore clinics now integrate gum health assessments into routine check-ups, reflecting the evolution toward proactive care.
How Patient Education Has Transformed Outcomes
Modern gum disease treatment places strong emphasis on patient involvement. Dentists actively educate patients about plaque control, lifestyle factors, and the importance of regular follow-up.
This collaborative approach empowers patients to take ownership of their oral health, improving treatment success and long-term stability.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Gum Disease Treatment
As research continues, gum disease treatment will likely become even more personalized. Ongoing advancements in diagnostics, biomaterials, and regenerative techniques promise improved outcomes with less intervention.
The shift toward prevention, early detection, and maintenance represents a lasting change in how dentists approach periodontal health.
Key Reflections on the Evolution of Gum Disease Care
The journey from basic cleaning to comprehensive periodontal management highlights how far dentistry has progressed. Modern gum disease treatment prioritizes preservation, comfort, and long-term health rather than reactive solutions.
Dental practices that embrace these principles—such as those aligned with patient-focused care models like Nuffield Dental, demonstrate how contemporary dentistry supports sustainable gum health through education, prevention, and ethical treatment planning.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How has gum disease treatment changed over time?
Treatment has evolved from basic cleaning and extractions to personalized, preventive, and minimally invasive periodontal care.
2. Is modern gum disease treatment more effective?
Yes, early detection, advanced diagnostics, and maintenance-focused care significantly improve outcomes.
3. Can advanced gum disease still be treated today?
While it cannot be fully reversed, modern treatments can stabilize the condition and preserve teeth.
4. Does everyone with gum disease need surgery?
No, many cases respond well to non-surgical treatment and structured maintenance.
5. How often should patients with gum disease see a dentist?
Patients may require visits every three to four months, depending on disease severity.