Ever since cell phones were invented people have spread rumors and gathered research on the topic, specifically around cell phones and brain cancer. Since cell phones emit a certain amount of radiation, and since they’re on our ears a lot, it’s a logical question. It’s not a new myth.
But is there any truth to it?
Well, not really.
Both the American Cancer Society and Cancer.gov have published research on the topic. In no part of their information does it conclude that cell phones cause brain cancer. While the scientific community is divided on the topic, there seems to be no definitive research that tracks cellular phones as the cause of brain cancer.
Cell phones emit radiation, as cell phones rely on microwave radiation. This is part of a non-ionizing region of the electromagnetic spectrum, ultraviolet light, gamma rays, and x-rays are the ionizing regions, which interfere with cell growth and alter genetic material. This is the radioactivity which is carcinogenic. Cellphone radiation is not carcinogenic; this is because the non-ionizing radiation is not known to direct interference with cellular processes.

Photo courtesy of the CDC
According to studies done, there is no significant correlation between cancer and use of cellphone that exists. Since cell phone signal boosters use the same microwaves, there is also no specific correlation between cancer and boosters.
One study, by Health Research Programme (MTHR) and Mobile Telecommunication, which majorly focused on cell phone and cell phone base station on people’s exposure. After the research, the results showed that there wasn’t any relationship between cancer and mobile phone use.
In 2010, the long-awaited results of interphone study were published. This was the largest case/control study up to date that explored the link between cancer and cell phones. According to the research, 13 countries over the period of 10 years had 5,117 brain tumor cases, there was reduction risk in many cell phone users for glioma and meningioma, but the greater elevated risk was reported to the glioma subjects using cell phones. Further, a greater risk for glioma people showed that much of the affected part was the side of the face where a phone is held mostly by the user.
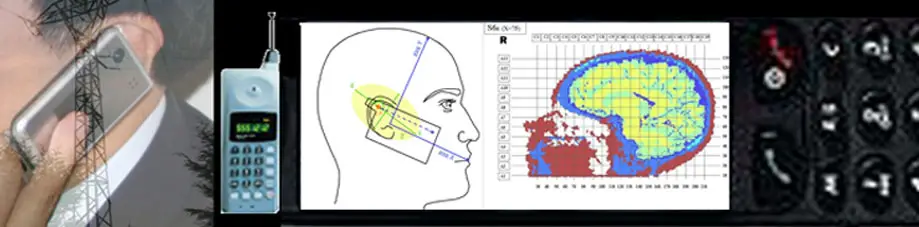
Further investigations were done in the search for the truth. In this study, an animal was used in a laboratory with the purpose to explore the effects of radio frequencies. As mentioned, non-ionizing radiation is emitted by cell phones and is not energetic enough to cause DNA damage directly.
A range of 450-2700 MHz, the radio frequency emitted by cellphones, is powerful enough to potentially trigger a chemical reaction. After the research in the laboratory animal, these radio frequencies didn’t show any link between the two that can be attributed to, or result in cancer. In another research done on rats, it indicated that these radio frequencies could possibly cause damage to the brain cells.
Because there is no conclusive evidence about these myths concerning cellphone and cancer, people should restrain from spreading these myths.