Researchers at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California and elsewhere determined that a relatively small number of DNA regions control a large portion of the physical differences between various breeds of dogs. The scientists hope that further study of these ...
Genetic Links to Human Longevity
Scientists at Boston University and Boston Medical Center in Massachusetts have discovered a group of genetic variants that can predict long life in humans with 77% accuracy. By examining the genomes of people over the age of one hundred, researchers ...
$30 Genome Possible
Researchers at Harvard University have developed a new method for sequencing the human genome leveraging the microdynamics of fluids – a method that could significantly decrease the cost of the procedure to as little as $30. By using small droplets ...
Genetic Links to Autism
Researchers at Oxford University in England have found a non-hereditary genetic link to autism. They have shown that individuals with autism tend to have either missing or extra sectors of DNA segments, a genetic mistake called copy number variants. This ...
Sea Lamprey’s Genome Mystery
Researchers have discovered that the sea lamprey, which emerged from jawless fish first appearing 500 million years ago, dramatically remodels its genome. Shortly after a fertilized lamprey egg divides into several cells, the growing embryo discards millions of units of ...
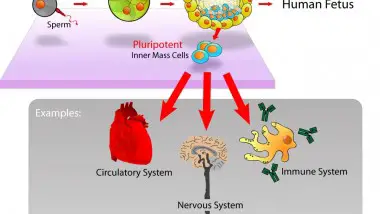
How Embryonic Stem Cells Become Tissue Specific
It has been unclear for many years how embryonic stem cells develop to their final destination as a specific tissue of the grown organism. Recently, a collaborative research group from the Hebrew University in Jerusalem, the US National Institutes of ...
Fat Gene Discovered
Researchers at William Harvey Research Institute and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry in London took part in an international consortium aimed at discovering new genetic variants that manipulate fat mass, weight, and the risk of obesity. The researchers’ ...
Genome of a Single Man Sequenced
Craig Venter, the man who first sequenced the human genome, has now sequenced his own genome. This is the first time a single person’s genome has been sequenced. The genomic sequence can tell a lot about a person, for instance ...